How SEO Works
How SEO Works
Have you ever wondered how Google decides which websites to show you when you search for something? It’s not magic. It’s a process called Search Engine Optimization, or SEO. If you’re a student, a blogger, or a small business owner, understanding this process can be a game-changer. This guide will explain exactly how SEO works in a simple, step-by-step way, even if you’re starting from zero. We’ll break down complex ideas into easy-to-understand concepts, helping you see how you can make your website more visible online.
This guide will cover everything from the basics of what search engines do to the specific steps you can take to improve your website’s ranking. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of the search engine optimization process and feel more confident about making it work for you.

Table of Contents
What is SEO and Why It Matters
Let’s start with the basics. SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. In simple terms, it’s the practice of improving your website so it shows up more often in search engine results. When people search for topics, products, or services related to what you offer, you want your site to be one of the first they see. That’s what good SEO does. You can learn more about the fundamentals in this guide on What is SEO.
But why does it matter so much? Think about your own habits. When you search for something on Google, how often do you click past the first page of results? Probably not very often. The top results get the vast majority of clicks. For a business, this means more website visitors, which can lead to more customers. For a blogger, it means more readers. For a job seeker, having a personal website that ranks well can impress potential employers.
SEO is a key part of a broader strategy called Digital Marketing for Beginners. While What is Digital Marketing covers many channels like social media and email, SEO focuses specifically on organic (non-paid) search traffic. This traffic is highly valuable because it comes from people who are actively looking for information or solutions that you provide. They have a specific need, and by appearing at the top of the search results, you present yourself as the best answer. This builds trust and credibility far more effectively than traditional advertising.
In short, SEO matters because it connects you with your target audience at the exact moment they are looking for you. It’s a powerful way to grow your online presence without paying for every single click.
How Search Engines Work
To understand how SEO works, you first need to understand how search engines themselves work. Imagine a search engine like Google as a massive digital library. This library contains copies of billions of web pages from all over the internet. When you type a search query, the search engine doesn’t scour the entire live internet in real-time. Instead, it quickly searches its own saved library to find the most relevant and helpful pages to answer your question.
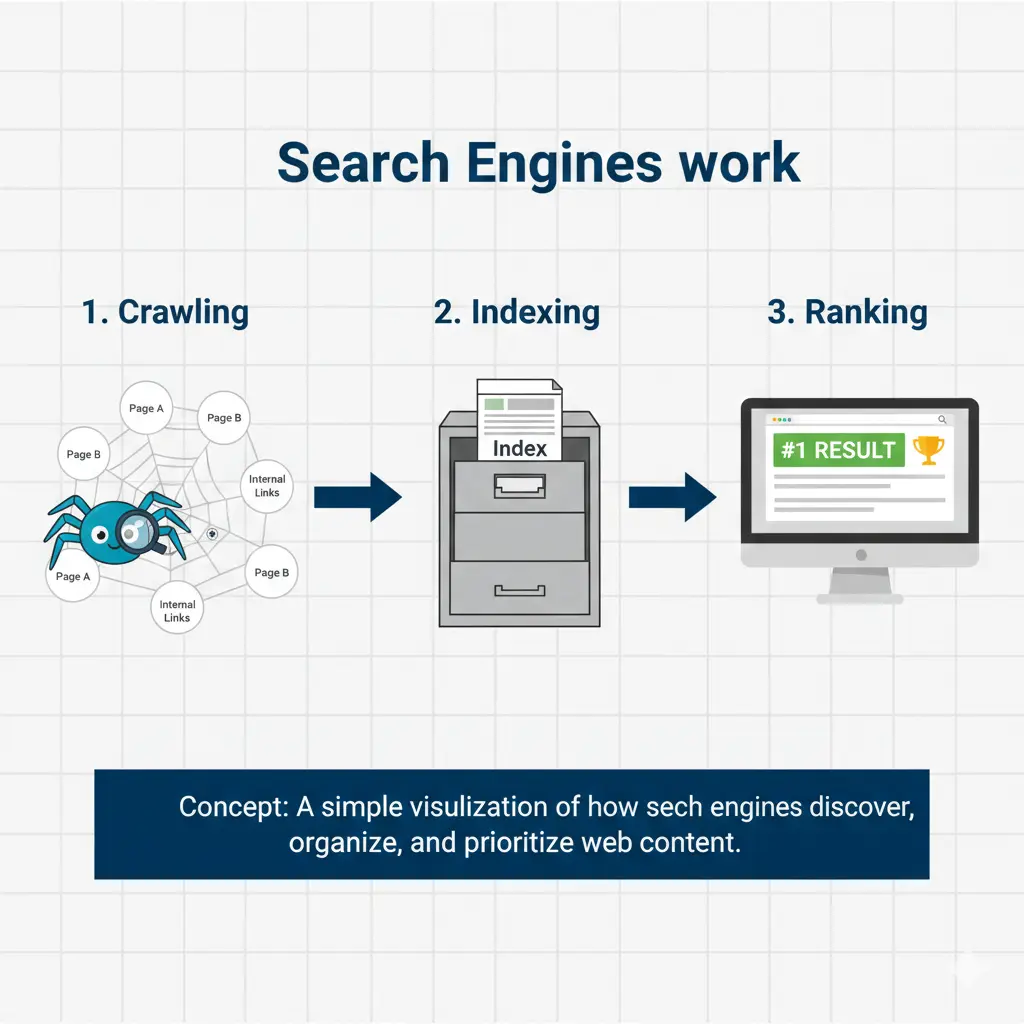
This process can be broken down into three main stages:
- Crawling: Search engines use automated programs called “crawlers” or “spiders” to discover new and updated pages on the web. These crawlers travel from link to link, constantly exploring the internet to find content.
- Indexing: After a page is discovered, the search engine analyzes its content—text, images, videos—and stores this information in a huge database called an index. This is like the library’s catalog. A page must be in the index to have any chance of appearing in search results.
- Ranking: When you perform a search, the search engine’s algorithm sifts through the indexed pages to find the ones that best match your query. It then ranks these pages from most relevant to least relevant and displays them to you.
The entire system is designed to provide you with the most useful, accurate, and high-quality results as quickly as possible. The job of an SEO professional is to make sure a website is easy for search engines to crawl, index, and, most importantly, rank highly for relevant searches. The search engine working process is a foundational concept for any aspiring SEO expert.
Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking Explained
Let’s dive a little deeper into the three core functions of a search engine: crawling, indexing, and ranking. Understanding each one is crucial for anyone learning SEO for beginners.
Crawling: The Discovery Phase
Crawling is how search engines discover content. Google’s crawlers, known as Googlebot, systematically browse the web. They start with a list of known web addresses from past crawls and sitemaps provided by website owners. As they visit these websites, they follow the links on those pages to find new ones. It’s like a spider exploring a web, which is why they are often called “spiders.”
For your website to be found, it needs to be accessible to these crawlers. If your site has pages that aren’t linked from anywhere else (known as orphan pages), crawlers may never find them. You can help crawlers by having a clear website structure with internal links connecting your pages. You can also submit a sitemap—a file that lists all the pages on your site—directly to Google through a free tool called Google Search Console.
Indexing: The Filing Phase
Once a page is crawled, the search engine needs to understand what it’s about. This is the indexing phase. During indexing, the search engine analyzes the content of the page, including the text, headings, images, and videos. It tries to figure out the main topics and keywords associated with the page.
All this information is then stored in a massive database called the search index. Think of it as a giant encyclopedia of the web. A page must be successfully indexed to be shown in search results. If a page has technical issues that prevent a search engine from reading its content, it might not get indexed properly, making it invisible to searchers. This process of website indexing is a critical checkpoint for your content.
Ranking: The Sorting Phase
Ranking is the final and most complex step. When you enter a search query, the search engine’s algorithm instantly goes to work. It searches its index for all the pages that could potentially answer your query. Then, it uses hundreds of different signals to decide which pages are the most relevant and authoritative. This is how Google ranks websites.
These ranking signals include:
- The words in your query: The most basic signal is whether the page contains the keywords you searched for.
- Relevance of content: The algorithm analyzes if the content comprehensively answers the searcher’s question.
- Quality of content: It looks for signals of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
- Usability of the page: This includes factors like mobile-friendliness and page speed.
- Backlinks: Links from other reputable websites act as “votes” of confidence, telling search engines that your content is valuable.
The crawling and indexing process gets your page into the library, but the ranking process determines which shelf it sits on—the top shelf or one that’s hidden in the back.
How Google Ranks Websites
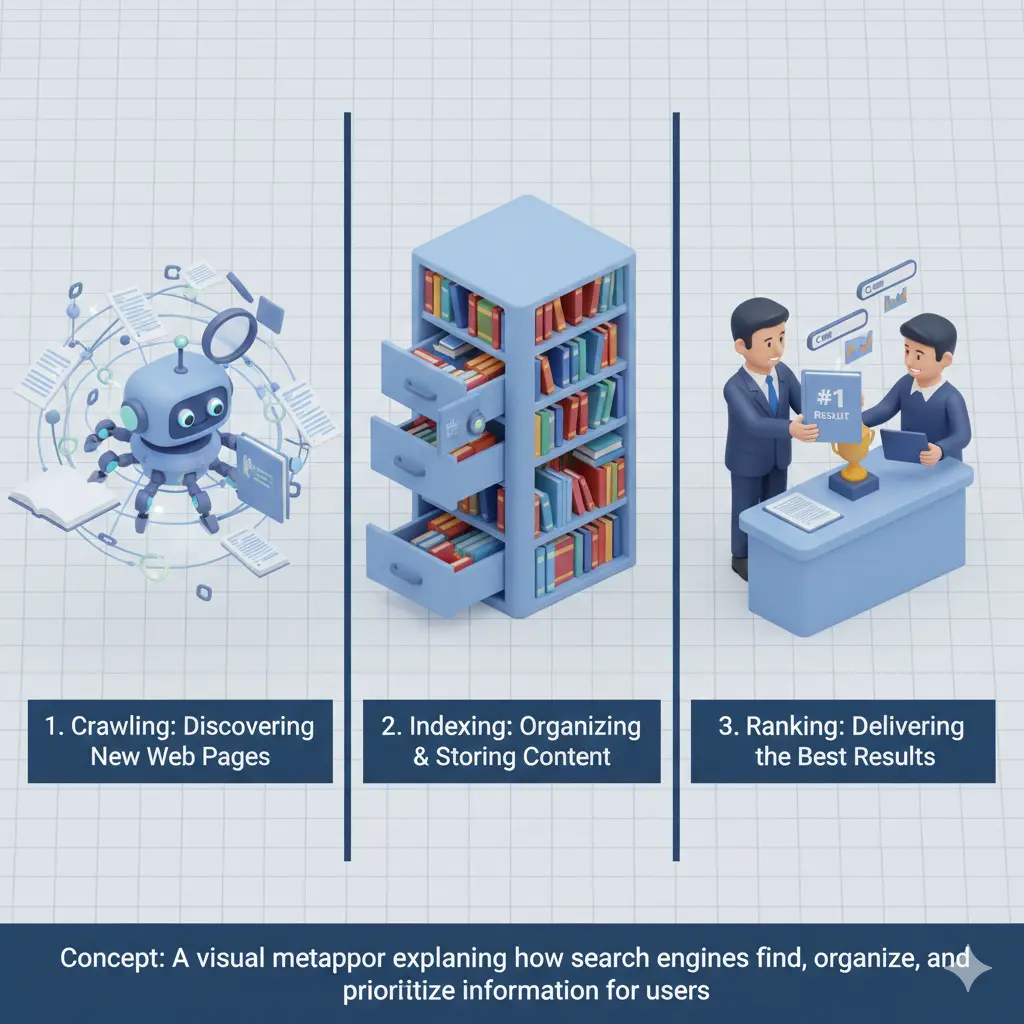
The secret to how websites rank on Google lies in its complex algorithm. While Google keeps the exact details of its google algorithm a closely guarded secret, it has shared a lot of information about what it considers important. The goal is always to provide the user with the best possible answer to their query.
Google uses a combination of over 200 ranking factors to sort through the billions of pages in its index. We can group these factors into several key areas:
Relevance and Content Quality
First and foremost, your content must be relevant to the search query. If someone searches for “how to bake a chocolate cake,” they expect to find a recipe, not a page about car engines. The algorithm analyzes the text on your page to see how well it matches the searcher’s intent.
But relevance isn’t enough. The quality of your content is paramount. Google wants to rank content that is:
- Helpful and Comprehensive: Does it fully answer the user’s question?
- Trustworthy: Is the information accurate and well-supported?
- Expertly Written: Is it clear that the author knows the topic well?
- Unique: Does it provide original information or a unique perspective?
A thin, poorly written page is unlikely to rank, even if it uses the right keywords.
Backlinks (Off-Page Signals)
Backlinks are links from other websites to your page. In Google’s eyes, a link from another site is like a vote of confidence. If many reputable, high-quality websites link to your page, Google sees this as a strong signal that your content is valuable and trustworthy. The quality of the links matters more than the quantity. One link from a major news site or a respected industry blog is worth more than hundreds of links from low-quality, spammy sites.
User Experience (On-Page Signals)
Google wants to send users to pages that are easy and pleasant to use. This is called user experience. Key factors include:
- Page Speed: How quickly does your page load? Users are impatient, and slow-loading pages lead to a poor experience.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Does your website work well on a smartphone? The majority of searches now happen on mobile devices, so this is essential.
- Readability: Is the content easy to read with clear headings, short paragraphs, and a clean layout?
- Website Security: Is your site secure (using HTTPS)? Google prefers to send users to secure websites.
Searcher’s Context
The algorithm also considers the user’s context, such as their location, search history, and settings. For example, if you search for “pizza restaurants” in New York, you will get different results than someone searching for the same term in London.
Understanding how Google ranks websites is about seeing the bigger picture. It’s not about tricking an algorithm. It’s about creating a great, helpful, and user-friendly experience for people.

Step-by-Step SEO Process
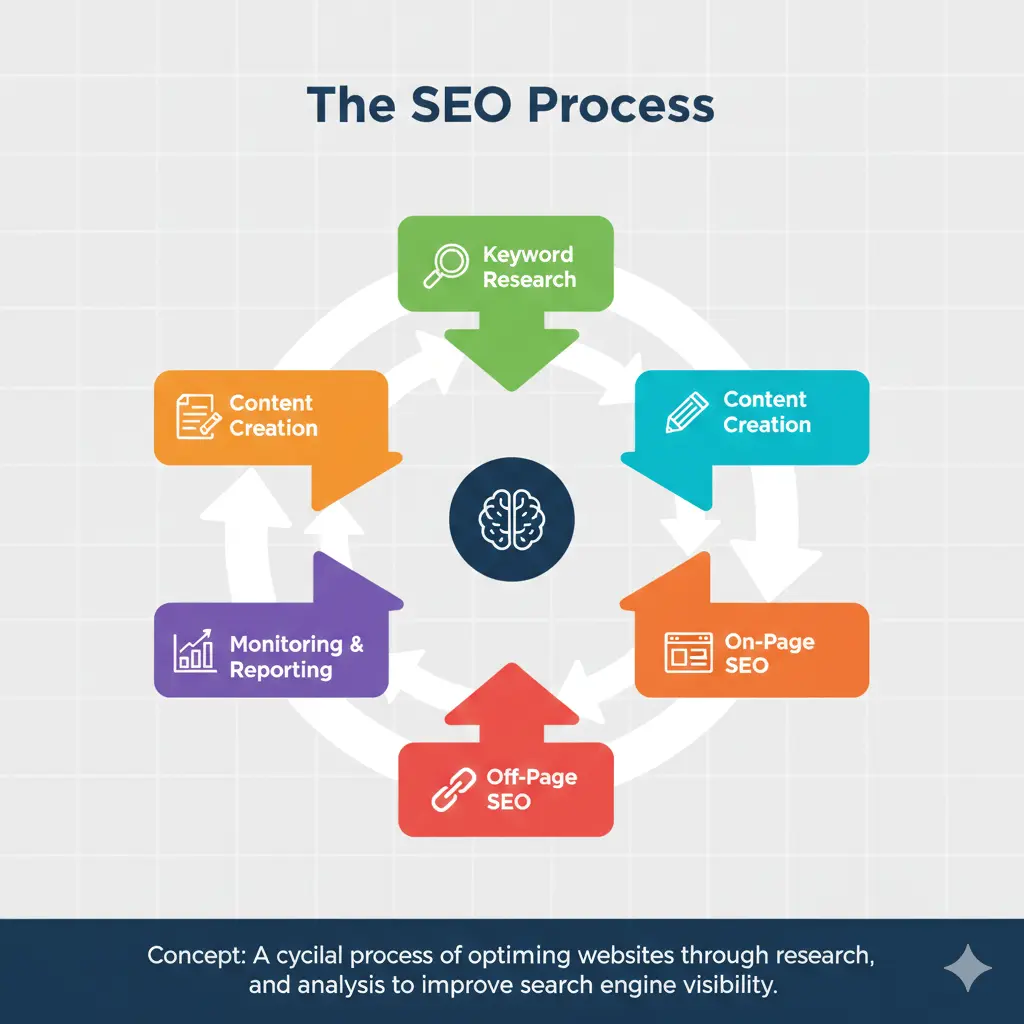
Now that you understand the theory, let’s look at the practical SEO process. While it can seem overwhelming, breaking it down into steps makes it much more manageable. The search engine optimization process is a cycle, not a one-time task.
Step 1: Keyword Research
Everything in SEO starts with understanding what your audience is searching for. Keyword Research is the process of finding the words and phrases (keywords) that people type into search engines. The goal is to find keywords that are relevant to your content, have a decent number of people searching for them (search volume), and aren’t overly competitive. For example, a small bakery might target “best gluten-free cupcakes in [Your City]” instead of the highly competitive keyword “cupcakes.”
Step 2: Content Creation
Once you have your keywords, the next step is to create high-quality content that addresses the searcher’s intent behind those keywords. If the keyword is “how to fix a leaky faucet,” your content should be a step-by-step guide that helps someone do exactly that. Your content should be comprehensive, well-written, and more helpful than what is currently ranking at the top. This is the heart of the SEO process.
Step 3: On-Page Optimization
After creating your content, you need to optimize it for search engines. This is known as On Page SEO. This involves:
- Placing your primary keyword in key places like the page title, main heading (H1), and the first paragraph.
- Writing a compelling meta title and meta description to encourage clicks from the search results page.
- Using descriptive headings (H2, H3) to structure your content and make it easy to read.
- Optimizing your images by using descriptive file names and alt text.
- Adding internal links to other relevant pages on your own website.
Step 4: Technical Optimization
Technical SEO focuses on improving the technical aspects of your website to help search engines crawl and index it more effectively. This includes:
- Ensuring your website loads quickly.
- Making sure your site is mobile-friendly.
- Creating an XML sitemap and submitting it to Google.
- Using a secure connection (HTTPS).
- Fixing any broken links or crawl errors.
Step 5: Off-Page Optimization (Link Building)
Off Page SEO refers to actions taken outside of your own website to impact your rankings. The most important part of this is link building—the process of acquiring backlinks from other websites. You can earn links by:
- Creating amazing content that people naturally want to link to.
- Guest posting on other relevant blogs.
- Reaching out to journalists and bloggers to share your content.
Step 6: Monitor and Analyze
SEO is not a “set it and forget it” activity. The final step is to monitor your results and analyze your data. Tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console (both free) can show you which keywords you’re ranking for, how much traffic you’re getting, and how users are behaving on your site. This data helps you understand what’s working and where you can improve, restarting the cycle.
Role of Keywords in SEO
Keywords are the foundation of SEO. They are the bridge between what people are searching for and the content you are providing to fill that need. When we talk about the role of keywords, it’s not about stuffing them into your content as many times as possible. That’s an old, outdated practice that will actually hurt your rankings.
Today, the role of keywords is about understanding user intent. User intent is the “why” behind a search query. Are they looking to learn something, buy something, or find a specific website?
We can generally categorize keywords into four types of intent:
- Informational: The user wants to find information. Examples include “how does photosynthesis work” or “what is the capital of Australia.” Blog posts, guides, and tutorials are great for targeting these keywords.
- Navigational: The user wants to find a specific website or page. Examples include “Facebook login” or “YouTube.”
- Commercial: The user is researching before making a purchase. They are comparing products or services. Examples include “best running shoes for men” or “iPhone vs. Samsung review.”
- Transactional: The user is ready to buy. Examples include “buy Air Jordan 1” or “cheap flights to London.”
Your job is to match your content to the right intent. If you have an e-commerce store, you’ll want to create product pages targeting transactional keywords. If you have a blog, you’ll focus on informational keywords.
Effective keyword strategy involves:
- Finding the Right Keywords: Using keyword research tools to find terms that your audience is using.
- Targeting a Primary Keyword: Focusing each page on one main keyword.
- Using Related Keywords: Naturally including synonyms and related terms (like we’ve used how google ranks websites and search engine working in this article) to give search engines more context about your page’s topic.
Keywords are not just words; they are insights into your audience’s needs and problems. By understanding and using them correctly, you can create content that truly serves your audience and ranks well in search results.
On-Page vs Technical vs Off-Page SEO
As we touched on in the SEO process, there are three main categories of SEO: On-Page, Technical, and Off-Page. Understanding the difference is key for beginners. Think of it like building a house.
On-Page SEO: The Content and Structure of the House
On-Page SEO includes everything you can directly control on your web pages to improve their rankings. This is about making your content clear to both users and search engines. It’s the quality of the materials you use to build your house and how you arrange the rooms.
Key activities include:
- Optimizing title tags and meta descriptions.
- Creating high-quality, relevant content.
- Using headings (H1, H2, H3) to structure your content.
- Optimizing images with alt text.
- Adding internal links to other pages on your site.
Good On-Page SEO tells Google exactly what your page is about.
Technical SEO: The Foundation and Utilities of the House
Technical SEO is all about the backend of your website. It’s the strong foundation, plumbing, and electrical wiring of your house. If the foundation is weak, the whole house is unstable, no matter how nice it looks inside. Similarly, if your site has technical problems, search engines will have a hard time crawling and indexing it, which means it won’t rank.
Key activities include:
- Improving website speed.
- Ensuring the site is mobile-friendly.
- Creating an XML sitemap.
- Using HTTPS for security.
- Fixing broken links and duplicate content issues.
Good Technical SEO makes your website easy for search engine crawlers to access and understand.
Off-Page SEO: The Reputation and Location of the House
Off-Page SEO refers to actions taken outside your website to build its authority and reputation. It’s like the location and neighborhood of your house. A great house in a bad neighborhood with no roads leading to it won’t get many visitors. Off-Page SEO builds the roads and the positive reputation that drives people to your site.
The most important aspect of this is building backlinks. Other signals include:
- Social media marketing.
- Brand mentions on other sites.
- Positive reviews on platforms like Google Business Profile.
A strong Off-Page SEO strategy tells Google that your website is a trusted authority in its field. All three types of SEO are essential. You can’t have one without the others and expect long-term success.
How AI and Algorithms Affect SEO
The world of SEO is constantly changing, and one of the biggest drivers of change today is Artificial Intelligence (AI). The google algorithm has become increasingly sophisticated, using machine learning and AI to better understand language and user intent.
One of the most significant AI-powered updates was Google’s RankBrain, and more recently, the Multitask Unified Model (MUM) and other AI systems. These systems help Google understand complex queries and the nuances of human language. This means Google can better grasp the context of a page, not just the keywords it contains. For a beginner, this reinforces a simple but powerful idea: write for humans, not for robots. The more helpful and natural your content is, the better it will perform in an AI-driven search world.
AI is also changing how SEO is done. There are now AI SEO tools that can help with tasks like:
- Generating content ideas.
- Writing drafts of articles.
- Finding keyword opportunities.
- Analyzing competitors.
However, it’s important to use AI as a tool, not a replacement for human strategy and creativity. AI-generated content often lacks the expertise, personal experience, and trustworthiness that Google values. The best approach is to use AI to assist your workflow, but always have a human expert review, edit, and add unique value to the content.
Furthermore, AI is powering new search experiences like Google’s AI Overviews, which provide direct answers at the top of the results page. To be featured in these, your content needs to be clear, factual, and directly answer common questions.
Common SEO Mistakes Beginners Make
When you’re just starting with SEO, it’s easy to make mistakes. Here are some of the most common pitfalls to avoid:
- Keyword Stuffing: As mentioned earlier, repeating your keyword over and over again in an unnatural way is a big mistake. It makes your content hard to read and can lead to a Google penalty. Focus on writing naturally.
- Ignoring User Intent: Choosing a keyword and writing about a topic that doesn’t match what the user is actually looking for. Always ask yourself, “What does someone searching this term want to find?”
- Focusing Only on On-Page SEO: Many beginners spend all their time tweaking their content but completely ignore Technical and Off-Page SEO. A beautiful page won’t rank if it loads slowly or has no backlinks.
- Buying Backlinks: It can be tempting to pay for links to speed up the process, but this is a violation of Google’s guidelines. It can get your site penalized or even removed from search results. Earn links, don’t buy them.
- Not Being Patient: SEO takes time. You won’t see results overnight. Many beginners give up after a few weeks because they don’t see an immediate traffic boost.
- Ignoring Mobile: Forgetting to check how your website looks and functions on a smartphone. With most users on mobile, a poor mobile experience is a major ranking problem.
- Publishing Thin or Low-Quality Content: Creating many short, unhelpful articles instead of a few high-quality, comprehensive ones. Quality always beats quantity in SEO.
Avoiding these common errors will put you far ahead of many other beginners in the SEO for beginners journey.
How Long SEO Takes to Show Results
This is one of the most common questions in SEO, and the honest answer is: it depends. SEO is a long-term strategy, not a quick fix. You should not expect to see significant results in the first few weeks.
Generally, you can expect to start seeing some positive movement in your rankings and traffic within 4 to 6 months. To achieve significant, game-changing results, it can often take 6 to 12 months or even longer.
Several factors influence how long it takes:
- Competition: If you’re in a highly competitive industry with big, established players, it will take longer to rank.
- Website Age and Authority: A brand-new website with no history or backlinks will take longer to gain trust from Google than an older, more established site.
- Your Budget and Resources: The amount of time and money you can invest in content creation and link building will affect the speed of your results.
- The State of Your Website: If your site has a lot of technical issues that need to be fixed first, that will add to the timeline.
The key is to be consistent. Keep creating great content, optimizing your site, and building quality backlinks. SEO is like planting a tree. You have to water it and care for it for a long time before you can enjoy its shade. But the wait is worth it, as the organic traffic it generates is sustainable and highly valuable.
FAQ
Yes, absolutely! There are many free resources and tools available online (like this guide!). With time and a willingness to learn, anyone can grasp the basics of SEO and start implementing them on their website. For more complex sites or competitive industries, you might eventually want to hire a professional, but you can certainly get started on your own.
SEO (organic traffic) and paid ads (like Google Ads) both have their place. Paid ads can get you traffic instantly, but you have to pay for every click, and the traffic stops as soon as you stop paying. SEO takes longer to work, but once you rank, you can get "free" traffic around the clock. A good digital marketing strategy often uses both.
While not strictly necessary for every type of website, having a blog is one of the most effective ways to improve your SEO. A blog allows you to regularly create fresh content, target a wide range of informational keywords, and build authority in your niche. It gives you more opportunities to rank and attract backlinks.
You should focus each page on one primary keyword. You can and should also include several related keywords and synonyms naturally throughout the content. There is no magic number. The goal is to cover a topic comprehensively, not to hit a specific keyword density.
You will hear this question every few years. SEO is not dead, but it is constantly evolving. The tactics that worked 10 years ago are now obsolete. As long as people use search engines to find information, there will be a need to optimize content to be found. The principles of creating high-quality, user-focused content will always be relevant.

